
Edito operating advice Tire
Zoom sur les roues d'un camion équipé en pneus Michelin
Usage Tips
MOUNTING TRUCK AND BUS TIRES INTRODUCTION
Installation is completed once tire compatibility is verified with vehicle manufacturer's recommendations. Correct tire usage should comply with recommended operating procedures and in compliance with safety regulations. Following these recommendations will allow the use of a tire's full potential, while providing a safe work environment for personnel.
A. General Precautions
- Operators must be equipped with their personal protective equipment (PPE: ear plugs, gloves, safety shoes, safety glasses, etc.).
- Operators must have a safe working environment.
- Operators must ensure that the vehicle is stationary, its engine is turned off and the vehicle is properly secured (parking brake, wheel chock, jack, etc.)
B. Tire Installation Precautions
- Make sure that the wheel and its components are in good condition.
- Ensure tire-wheel, tire-vehicle and tire-use compatibility.
- Observe tire positions: mounting direction, direction of rotation and other instructions if noted on the side of the tires.
- Make sure the inside of the tire is clean, dry and free of any foreign objects. For a tire that has already been used, carefully check that the inside of the tire does not show signs of under-inflation (marbling, dislocations, etc.).
- Change the valve seal or valve.
- Ensure safe inflation by following the inflation steps. Make sure all components are in place. Never stand in front of a mounted tire, instead stand in line with the tread at a distance of at least 10 feet.
- Follow these precautions are for new tires and tires that have already been used.
- For vehicles equipped with disc brakes, we recommend mounting tires on wheels with a protected valve, to avoid the risk of damage to the valve from an object becoming caught between the brake and wheel.
Incorrect installation can cause damage to the tires, vehicle or other people (serious or even fatal injuries).
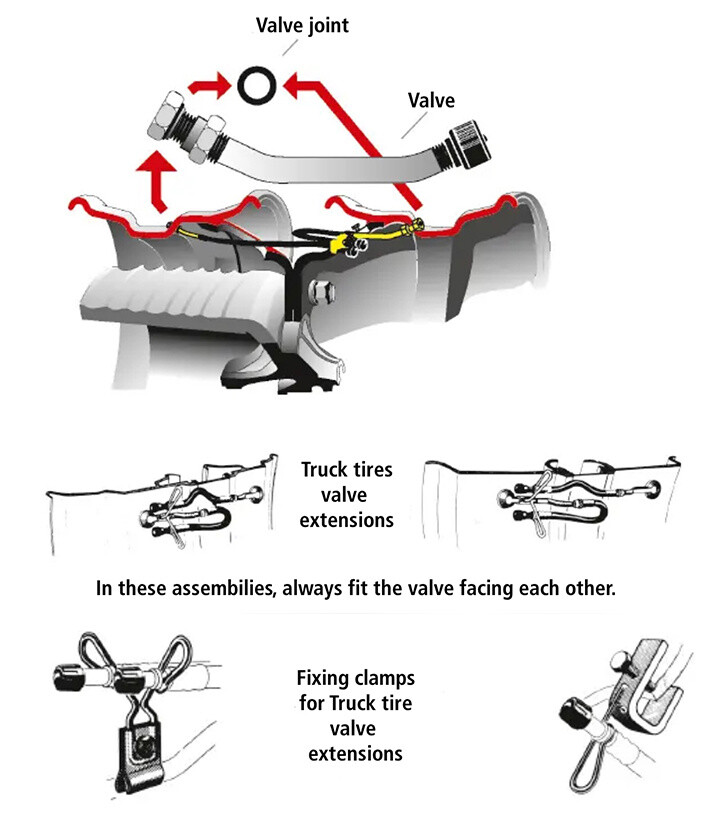
C. Checking the valves
Due to high temperatures and brake aging, valve seals and inflation extensions must be replaced during each tire change. A valve cap in excellent condition is essential to preserve the seal.
Picto valve Help and advice

maintenance page 27 bis
Sealing diagram for dual tires. For this assembly type, always position the valves face-to-face.
PROPER TIRE INFLATION INSTRUCTIONS
This action must be completed by trained staff using proper equipment. Improper installation can damage the tire (which may not be visible at the time of installation), the inner tube or the wheel.
Cold tire inflation pressure must be set in accordance with the load, speed and usage conditions.
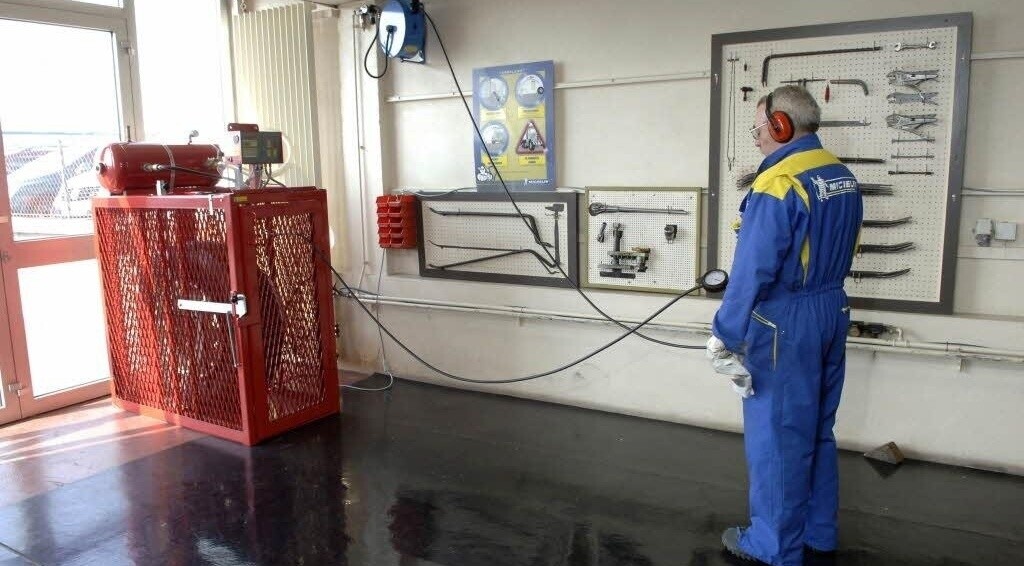
Michelin recommends that tires are inflated using an “inflation cage.”
Inflation must be carried out in two stages:
First stage:
• Pre-inflate to 22 psi
• Examine the tire, if in doubt stop and call a specialist

Edito la juste pression photo principale Help and Advice
During inflation, position yourself in line with the tread and at least 10 feet away.
Second Stage:
• Inflate to the correct pressure
• Place tire vertically in the inflation cage or in a prepared area
BALANCING
It is important to ensure tires are properly balanced. To:
• Increase mileage longevity
• Prevent premature mechanical wear and tear
• Guarantee vehicle driving performance
WHEEL TIGHTENING
The right wheel torque keeps the mechanical components and the tire contact patch in good form, keeping you safe.
A. Wheel Condition:
- Wheel condition must be checked regularly. A cracked wheel or rim must be replaced.
- Preferably, wheels or rims should not be repaired by welding.
- If welding is required, the tire must be removed from the rim. If not, the risk of explosion is very high.
- The tire can be reassembled when all parts return to room temperature.
- Before welding the vehicle chassis, the tire and wheel units must be removed.
- When dismantling multiple wheels, we recommended deflating all vehicle tires.
B. Before tightening, it is necessary to:
1. Clean:
- The contact surface of the hub and wheel.
- Studs and nuts.
2. Check:
- The condition of the mounting holes (deformations, cracks, etc.).
- The condition of the studs (deformations, condition of the threads, etc.).
- The condition of the nuts (deformations, condition of the threads, etc.).
- If necessary, remove rust and paint residues with a wire brush.
- Possible metal deburring.
3. Lubricate:
- With a drop of oil on the nut threads and studs, and of flat or spigot nuts.
- Never lubricate the nut contact surfaces, or spherical or M-type washers.
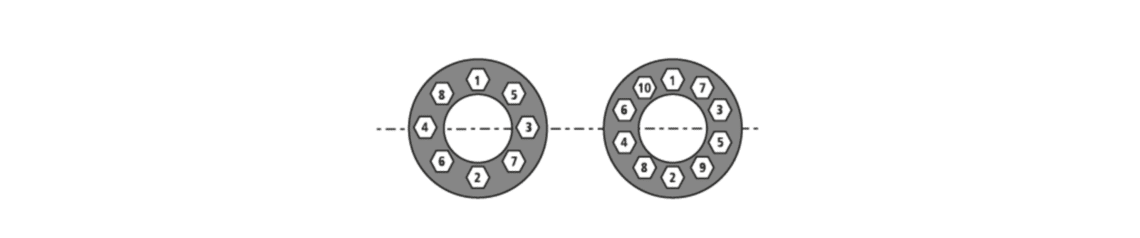
4. Final tightening torque:
- Must be done within the tightening torques recommended by the vehicle manufacturer.
- Depending on the number of nuts, please remember the cross-tightening order.
- Tightening to the correct torque enables easy disassembly in the event of a puncture. Also, it will prevent axle damage and ensures your safety.
Picto Schema maintenance clamp Help and Advice
Overtightening can be as damaging as under-tightening, which can lead to:
- Damage and/or broken axles.
- Wheel loss due to damage of nut threads.
- Drum warping, etc.
After 30 minutes or a distance of 50 to 100 kilometers (30 to 60 miles), the wheel nuts must be checked again using a properly calibrated torque wrench. When checking the torque, do not tighten and retighten.
MONITORING AND MAINTENANCE
Tires must be checked regularly. Before an inspection, make sure that the vehicle is completely stopped with the engine switched off.
A. Tire Maintenance
• Michelin recommends checking:
- Any irregular wear, punctures, cuts, visible tread deformations, sidewalls or grip area of the tire.
- Any damage to the rim with a tire professional.
• The causes of handling problems (e.g. pulling to the left or right, comfort problems due to vibrations, etc.) must be investigated.
• If a loss of pressure occurs, it is imperative to stop as soon as possible. Driving on under-inflated tires can lead to thermal deterioration of tire components.
• The tire must be removed from the rim to determine the cause of pressure loss.
• Any damage should be examined by a tire professional who can determine if repair is necessary or possible.
• Repairs must be carried out by a tire specialist who will complete the repair.
• Prior to any repair, the inside of the tire must be examined for damage.
B. Tire Inspection and Recommendations
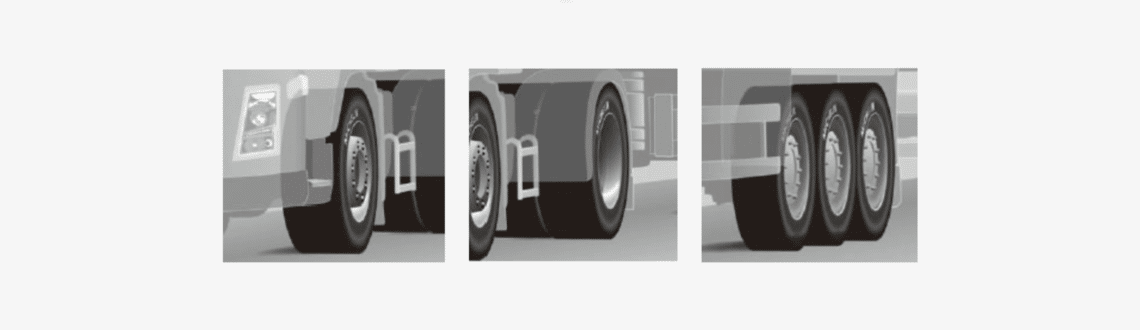
Picto Image truck axles Help and Advice
From left to right, axles: Front (F), Drive (D), Trailer (T)
C. Switching and Reversing
Switching consists of disassembling the wheel from one position of the vehicle and reassembling it in another position. Rim turnaround consists of removing the tire from the rim and reassembling it in the opposite direction. These two actions can increase tire efficiency by approximately 20%.
In order to optimize intended tread pattern use, please check to see if a tire has directional tread. In such cases, it is necessary to turn and swap all the axle casings to maintain the same direction of travel.

picto edito maintenance page 34 help and advice
Alignment
Correct alignment makes it possible to maintain the tire's mileage performance. Adjustment of all vehicle axles can save an average of 20% in tire mileage and an average of 2% in fuel savings. (Source Josam Alignment)
TIRE REMOVAL PRECAUTIONS
When removing the wheel from the vehicle, if the tire is part of a dual system, or if there is obvious damage to the rim, tires must:
• Be deflated by removing the nozzle from the valve
• Be removed following vehicle manufacturer’s recommendations and instructions
Michelin does not recommend removing the tire with the wheel mounted on the vehicle. If extenuating circumstance prevent you from removing the wheel, deflate the tire completely by removing the valve cap.
STORAGE AND HANDLING
A. Correct tire storage conditions:
• In a clean, dry, well-ventilated room, away from direct sunlight and moisture.
• Away from chemicals, solvents or hydrocarbons likely to alter the rubber.
• Away from any sharp objects (metal tip, wood, etc.).
• Away from any heat source: flames, burning objects, or material that may spark or have electric discharges, and from any source of ozone (transformers, electric motors, welding stations, etc.).
• When storing in stacks, make sure that the tires are not damaged. If storing for a long time, rotate (invert the order of the tires in the stack), so that the oldest tires can be removed first.
• Avoid crushing tires under other objects.
• Storage:
- For short-term storage (up to 4 weeks), tires can be stored horizontally, one on top of the other, on wooden pallets. The height of the stack must not exceed 4 feet. After 4 weeks, tires should be inverted in the stack. When mounted, tires must be stored inflated in an upright position or on a storage cart in a single layer.
- For long term storage, tires should be stored on a storage cart in a single layer, vertically, at least 6 in off the ground. To avoid any damage, it's recommended to rotate tires once a month.
• Inner tubes:
- Tire inner tubes should be slightly inflated, sprinkled with plain talcum powder and placed in the tires, or deflated and stored in a storage cart in stacks no larger than 20 in. Slatted wooden pallets are not recommended, due to uneven surfaces.
- If inner tubes are unopened, leave inner tubes in manufacturer's packaging, as the packaging provides protection against contamination, oxygen and the light/sun damage.
• Flaps:
- Flaps should generally be placed in the tires with the inner tubes. But if they need to be stored separately, place lay flaps flat on clean shelves (dust, grease, and moisture free). Never hang them up, doing so may damage or stretch them.
B. When handling tires and accessories, operators must:
• Follow their company’s safety policies.
• Wear personal protective equipment.
• Use tools and materials that will not damage the tires.
C. Additional Michelin storage information:
• Tires stored for more than five years must be examined by trained professionals to determine whether they are fit for use.
• We strongly recommend stored tires should be inflated with nitrogen. If air is used, it must be as dry as possible. Check that a valve cap is installed on the valve.
• Vehicle tires that remain on the ground must be inflated to the vehicle's normal tire pressure. Every four months, the tires must be rotated by a quarter turn. Every six months, check and adjust the pressure as necessary. Each year, tires must be used for a certain distance to eliminate “flat spots."
• Tires on suspended vehicles should be deflated to half of the vehicle's normal tire pressure.
• Stored spare tires should be deflated to half of the vehicle's normal tire pressure.
• Ensure proper procedures are in place to inspect and re-inflate tires once returned to service.
• Any stored tire must be visually inspected by qualified personnel before returning to service.
These tips and suggestions may also interest you:
• Tire Basics and Markings
• Tire Structure and Functions
• The Right Pressure




